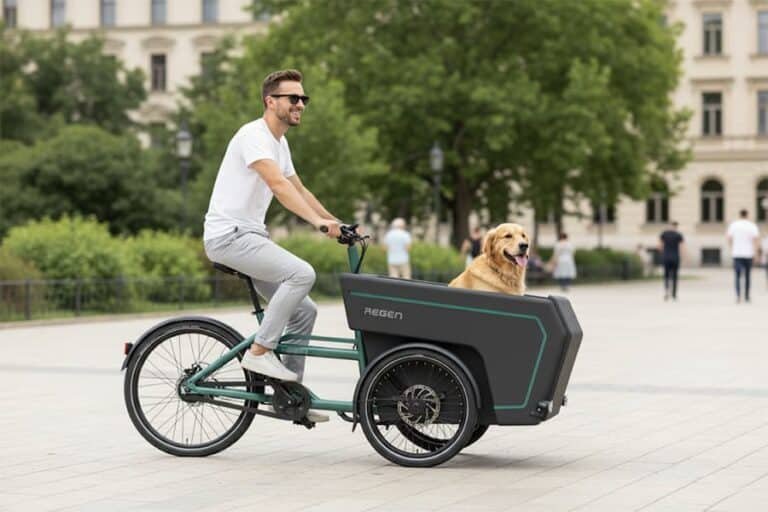
Rowery elektryczne (e-rowery) oferują wspomaganie pedałowania za pomocą dwóch głównych konfiguracji silnika: silniki piastowe I silniki środkoweSilniki piastowe są zintegrowane z piastą koła, z przodu lub z tyłu, zapewniając bezpośredni napęd. Natomiast silniki środkowego napędu są umieszczone centralnie przy suporcie roweru, współpracując z przerzutkami roweru, aby dostarczać moc.
Podczas opracowywania linii produktów e-bike wybór odpowiedniego silnika jest kluczową decyzją. Niezależnie od tego, czy projektujesz rower cargo, który potrzebuje dużego momentu obrotowego do ciężkich ładunków, czy rower elektryczny dojeżdżający do pracy, który stawia na wydajność i wagę, typ silnika bezpośrednio wpływa na wydajność, koszt i wrażenia użytkownika. Silniki z napędem środkowym i piastą dominują na rynku — ale poza specyfikacjami, co te wybory oznaczają dla strategii produktowej Twojej marki?
W tym artykule omówimy kluczowe różnice między silnikami mid-drive i hub, analizując ich zalety, ograniczenia i najlepsze przypadki użycia. Niezależnie od tego, czy optymalizujesz wydajność, koszty czy pozycję rynkową, ten przewodnik pomoże Ci podjąć świadomą decyzję.
Czym jest silnik centralnie umieszczony?
A silnik środkowy jest silnikiem wspomagania elektrycznego umieszczonym w rowerze obszar suportu, w pobliżu korby. W przeciwieństwie do silników piastowych, które napędzają koło bezpośrednio, silnik środkowy przekazuje moc poprzez łańcuch lub pasek napędowy roweru, pracując w synchronizacji z systemem przekładni. Ta konfiguracja zapewnia bardziej naturalne odczucie pedałowania i pozwala na lepsze rozłożenie momentu obrotowego, co czyni ją wysoce wydajną w różnych warunkach jazdy.
Ten "średni" W napęd środkowy odnosi się do jego centralne umiejscowienie na ramie roweru, zapewniając zrównoważony rozkład masy i lepsze prowadzenie. Ponieważ dostarcza moc poprzez układ napędowy, może wykorzystać przełożenia roweru, automatycznie dostosowując moment obrotowy i moc wyjściową do różnych terenów. Dzięki temu silniki o średnim napędzie są szczególnie odpowiednie do rowerów cargo, wysokowydajnych rowerów elektrycznych i zastosowań wymagających większej wydajności energetycznej.
W ostatnich latach technologia napędu środkowego znacznie się rozwinął, stając się mocniejsze, lżejsze i coraz bardziej energooszczędneWiodący producenci nieustannie udoskonalają te silniki, zwiększając ich wydajność i czyniąc je preferowanym wyborem marki rowerów elektrycznych premium skoncentrowaliśmy się na optymalnych wrażeniach z jazdy i długoterminowej trwałości.

Zalety silników z napędem pośrednim w Rowery cargo:
1. Wydajne przenoszenie mocy: Środkowy silnik działa bezpośrednio na układ pedałów, a współczynnik konwersji energii na ruch jest zazwyczaj wyższy niż 80%. W porównaniu do tradycyjnych silników piastowych, które mają wydajność 70-80%, środkowy silnik jest bardziej wydajny.
2. Obniżona odporność: Wewnętrzna konstrukcja zapadki sprzęgła w silniku środkowym umożliwia całkowite odłączenie go od zapadki suportu, gdy nie jest zasilany, eliminując opór magnetyczny. Dlatego nawet gdy akumulator jest rozładowany, kierowca może nadal jechać płynnie bez żadnego oporu.
3. Wyższy moment obrotowy: Środkowy silnik wykorzystuje wewnętrzny mechanizm zmiany biegów. Wiele sprzęgieł wewnątrz obudowy silnika tworzy przełączalną zapadkę, która zwiększa moment obrotowy, zapewniając większą moc przy obciążeniu i wspinaczce.
4. Rozsądne rozłożenie ciężaru: Dzięki umieszczeniu silnika w środkowej części ramy środek ciężkości pojazdu jest bardziej zrównoważony, co poprawia stabilność i prowadzenie podczas jazdy.
5. Projekt o wysokiej integracji: Zintegrowana, ujednolicona konstrukcja silnika umieszczonego centralnie skutkuje mniejszą liczbą połączeń kablowych, mniejszą liczbą akcesoriów, łatwiejszą konserwacją i czystszym wyglądem.
6. Zwiększona wydajność ochrony: Obudowa silnika środkowego ma zazwyczaj bardzo wysokie zdolności obronne, osiągając zazwyczaj poziom ochrony IP65 lub wyższy. Silnik, gdy jest w użyciu, może w pełni oprzeć się wtargnięciu zewnętrznych obiektów i pyłu, a także strumieniom wody pod niskim ciśnieniem z dowolnego kąta.
Wady silników centralnie umieszczonych w rowerach cargo:
1. Zwiększone zużycie układu napędowego:Dodatkowe obciążenie łańcucha i kół zębatych może prowadzić do przyspieszonego zużycia, co wymusi częstszą konserwację.
2. Wyższe koszty i złożoność:Systemy napędu środkowego są zazwyczaj droższe i wymagają bardziej skomplikowanej instalacji i konserwacji w porównaniu z silnikami w piaście.
3. Zależność od integralności układu napędowego:Jeśli łańcuch się zerwie, silnik nie będzie mógł pomóc, co może skutkować unieruchomieniem rowerzysty — co jest poważnym problemem przy przewożeniu ciężkiego ładunku.
Czym jest silnik piastowy?
Silnik piastowy, często nazywany silnikiem w kole, to silnik elektryczny zintegrowany z piastą koła, zapewniający bezpośredni napęd bez potrzeby stosowania zewnętrznych elementów przekładni, takich jak łańcuchy lub paski. Ta konstrukcja jest powszechna w różnych pojazdach elektrycznych, zwłaszcza rowerach elektrycznych (e-rowery), ze względu na swoją prostotę i wydajność.

Rodzaje silników piastowych
Silniki piastowe można klasyfikować na podstawie kilku czynników:
1. Typ silnika: szczotkowy czy bezszczotkowy
• Silniki szczotkowe piastowe: Wykorzystują szczotki do przewodzenia prądu do uzwojeń silnika. Choć są prostsze i często tańsze, zużywają się szybciej i wymagają większej konserwacji.
• Silniki piastowe bezszczotkowe:Silniki te są powszechnie stosowane w nowoczesnych rowerach elektrycznych. Wykorzystują sterowniki elektroniczne do kierowania prądu do uzwojeń, co przekłada się na większą wydajność, mniejsze wymagania konserwacyjne i dłuższą żywotność.
2. Umiejscowienie: Silniki piasty przedniej i tylnej
• Silniki piasty przedniej: Zamontowane na przednim kole silniki te dają wrażenie bycia ciągniętym. Są one zazwyczaj łatwiejsze w instalacji i konserwacji, ale mogą oferować mniejszą przyczepność, szczególnie na śliskich nawierzchniach.
• Silniki piasty tylnej: Znajdują się na tylnym kole i dają wrażenie pchania. Silniki w piaście tylnej zazwyczaj zapewniają lepszą przyczepność i są powszechniejsze w projektach rowerów elektrycznych.
3. Mechanizm napędowy: Napęd bezpośredni kontra silniki piastowe z przekładnią
• Silniki piastowe z napędem bezpośrednim (bez przekładni): Te silniki nie mają wewnętrznych przekładni; zewnętrzna powłoka silnika obraca się, aby bezpośrednio napędzać koło. Są większe, cięższe i zapewniają płynną, cichą pracę przy minimalnej konserwacji. Silniki z napędem bezpośrednim są szczególnie wydajne przy dużych prędkościach i są często stosowane w rowerach elektrycznych klasy 3 (speed pedelec).
• Silniki piastowe z przekładnią: Silniki te, wyposażone w wewnętrzne przekładnie planetarne, pozwalają silnikowi obracać się z większą prędkością obrotową, jednocześnie zmniejszając prędkość obrotową koła, co skutkuje większym momentem obrotowym. Są zazwyczaj mniejsze, lżejsze, bardziej wydajne i lepiej radzą sobie ze wspinaniem się na wzniesienia niż silniki z napędem bezpośrednim. Mają jednak więcej ruchomych części, które mogą wymagać konserwacji z czasem.
Dalsza lektura: Różnice między silnikami piasty roweru elektrycznego z napędem bezpośrednim i przekładniowym
Silniki piastowe w rowerach cargo
Rowery cargo są zaprojektowane do przewożenia dużych ładunków, co sprawia, że wspomaganie silnika jest szczególnie korzystne. Wybór między silnikami piastowymi a silnikami środkowymi w rowerach cargo zależy od różnych czynników, w tym kosztów, konserwacji i wymagań dotyczących wydajności.
Zalety silników piastowych w rowerach cargo:
- OpłacalnośćSilniki w piaście są zazwyczaj tańsze od silników umieszczonych centralnie, co czyni je atrakcyjną opcją dla konsumentów zwracających uwagę na budżet.
- Prostota i niskie koszty utrzymania: Silniki piastowe mają prostą konstrukcję i mniejszą liczbę ruchomych części, przez co wymagają mniej konserwacji, a jazda staje się bezproblemowa.
- Niezależne działanie układu napędowego: Silniki piastowe działają niezależnie od układu napędowego roweru, co pozwala rowerowi nadal funkcjonować, nawet jeśli łańcuch lub przerzutki zawiodą. Ta niezależność może być kluczowa podczas przewożenia ciężkich ładunków.
- 1TP2 Hamowanie oporowe:Niektóre silniki piastowe, szczególnie modele z napędem bezpośrednim, oferują hamowanie regeneracyjne, co może być korzystne przy kontrolowaniu prędkości na zjazdach i wydłużaniu żywotności akumulatora.
- Zgodność z napędami pasowymi i wewnętrznymi układami przekładniowymi: Silniki piastowe doskonale współpracują z napędem pasowym i piastami z przekładnią wewnętrzną, co pozwala na uzyskanie niemal bezobsługowego układu napędowego.
Wady silników piastowych w rowerach cargo
1. Ograniczony moment obrotowy i zdolność pokonywania wzniesieńSilniki w piaście zwykle zapewniają mniejszy moment obrotowy w porównaniu z silnikami umieszczonymi centralnie, przez co są mniej skuteczne przy pokonywaniu stromych wzniesień, szczególnie podczas przewożenia ciężkich ładunków.
2. Rozkład ciężaru i obsługa:Umieszczenie silnika w piaście koła dodaje nieresorowanego ciężaru, co może negatywnie wpłynąć na prowadzenie i jakość jazdy. Ten rozkład ciężaru może być szczególnie trudny w przypadku rowerów cargo, w których równowaga jest kluczowa.
3. Wyzwania konserwacyjne:W przypadku przebicia opony lub konserwacji koła, silniki piasty komplikują proces, przez co naprawa staje się bardziej uciążliwa w porównaniu z kołami bez silnika.
4. Obniżona wydajność: Silniki piastowe działają niezależnie od biegów roweru, co prowadzi do mniej wydajnego wykorzystania energii, szczególnie na zróżnicowanym terenie. Ta nieefektywność może skutkować skróceniem żywotności baterii i zmniejszeniem zasięgu.
5. Problemy z trakcją:Silniki w piaście przedniej mogą mieć zmniejszoną przyczepność, szczególnie na luźnych lub śliskich nawierzchniach, co może być problematyczne przy ruszaniu z miejsca lub podjeżdżaniu pod górę z obciążonym rowerem cargo.
Oto przejrzyste porównanie silników umieszczonych centralnie i silników w piaście w rowerach cargo:
| Funkcja | Silnik środkowy | Silnik piasty |
| Moment obrotowy i wspinaczka | Wykorzystuje przełożenia roweru, zapewniając większy moment obrotowy i lepszą wydajność na pochyłościach, co jest niezwykle ważne przy transporcie ciężkich ładunków. | Zazwyczaj zapewniają mniejszy moment obrotowy, przez co są mniej skuteczne przy pokonywaniu stromych wzniesień, szczególnie przy przewożeniu ciężkich ładunków. |
| Rozkład masy | Umieszczenie ich w centralnym miejscu przyczynia się do obniżenia środka ciężkości, co zwiększa stabilność i łatwość prowadzenia — kluczowe czynniki przy manewrowaniu rowerami cargo. | Dodaje ciężar do koła, zwiększając masę nieresorowaną, co może negatywnie wpłynąć na prowadzenie i jakość jazdy. Ten rozkład ciężaru może być szczególnie trudny w rowerach cargo, gdzie równowaga jest kluczowa. |
| Konserwacja | Może prowadzić do przyspieszonego zużycia łańcucha i kół zębatych, co wymusi częstszą konserwację. | Z uwagi na mniejszą liczbę ruchomych części silniki piastowe wymagają mniej konserwacji, co jest zaletą w przypadku rowerów cargo, które mogą być intensywnie użytkowane. |
| Koszt i złożoność | Są zazwyczaj droższe i wymagają bardziej skomplikowanej instalacji i konserwacji w porównaniu z silnikami piastowymi. | Są tańsze i łatwiejsze w instalacji, co czyni je atrakcyjną opcją dla konsumentów zwracających uwagę na budżet. |
| Efektywność | Działa wydajniej przy różnych prędkościach i rodzajach nawierzchni, wykorzystując przerzutki roweru, co potencjalnie wydłuża czas pracy akumulatora. | Działa niezależnie od biegów roweru, co przekłada się na mniej efektywne wykorzystanie energii, szczególnie na zróżnicowanym terenie. Może to skutkować skróceniem żywotności akumulatora i ograniczeniem zasięgu. |
| Trakcja | Zapewnia lepszą przyczepność, szczególnie na pochyłościach, dzięki możliwości efektywnego wykorzystania przełożeń roweru. | Silniki w piaście przedniej mogą mieć zmniejszoną przyczepność, szczególnie na luźnych lub śliskich nawierzchniach, co może być problematyczne przy ruszaniu z miejsca lub podjeżdżaniu pod górę z obciążonym rowerem cargo. |
Przewodnik zakupowy oparty na scenariuszach: Który z nich jest dla Ciebie bardziej odpowiedni?
W naszym nadchodzącym artykule zagłębimy się w oparty na scenariuszach przewodnik, który pomoże Ci wybrać najbardziej odpowiedni silnik do Twojego roweru elektrycznego. Jak trafnie ujął to jeden z inżynierów marki: „Nie ma idealnego silnika, tylko precyzyjne dopasowanie”. Aby pomóc Ci w podjęciu świadomej decyzji, przedstawimy Ci szybki schemat blokowy samooceny zatytułowany "Trzy kroki do znalezienia idealnego silnika"
- “Jak wybrać odpowiedni silnik do konkretnego roweru cargo“
- „Płaskie drogi miejskie, tereny pagórkowate lub górzyste, tereny mieszane”:Wybór odpowiedniego silnika“
- ” Każdy Ukryte rozważania przy wyborze silnika?”
W końcu,
Wybór odpowiedniego silnika może być trudny, nawet przy podstawowej wiedzy. Jeśli opracowujesz nowy model roweru elektrycznego cargo i potrzebujesz dopasowanego rozwiązania, zespół Regen jest do Twojej dyspozycji. Wystarczy skontaktować się z Zespół Regen. Po udzieleniu odpowiedzi na kilka kluczowych pytań, dostarczymy kompleksowy Rozwiązanie do personalizacji rowerów Cargo Bike i produkt gotowy do użycia.